
Health Food Deterrent to Fat Loss
Generally fruits are considered nutritious and a important portion of a diet to maintain a modest appetite. Adequate portions of fruit can be beneficial in providing vitamins and minerals not found in other foods.
Fruits are also less calorie dense in comparison with most other foods, which is why it’s considered essential for lowering body mass.
For the longest time the caloric content of foods have been valued as the most important, since the law of thermodynamics was the principle that had the highest priority regarding weight gain or weight loss.
While this principle was relevant, newer research showed that thermodynamics was not mutually exclusive. Factors of circulating insulin, leptin, and ghrelin hormones also further contribute to weight management.
Fruits are low in calories but vary greatly with the content of sugar that has an impact on blood insulin levels once consumed.
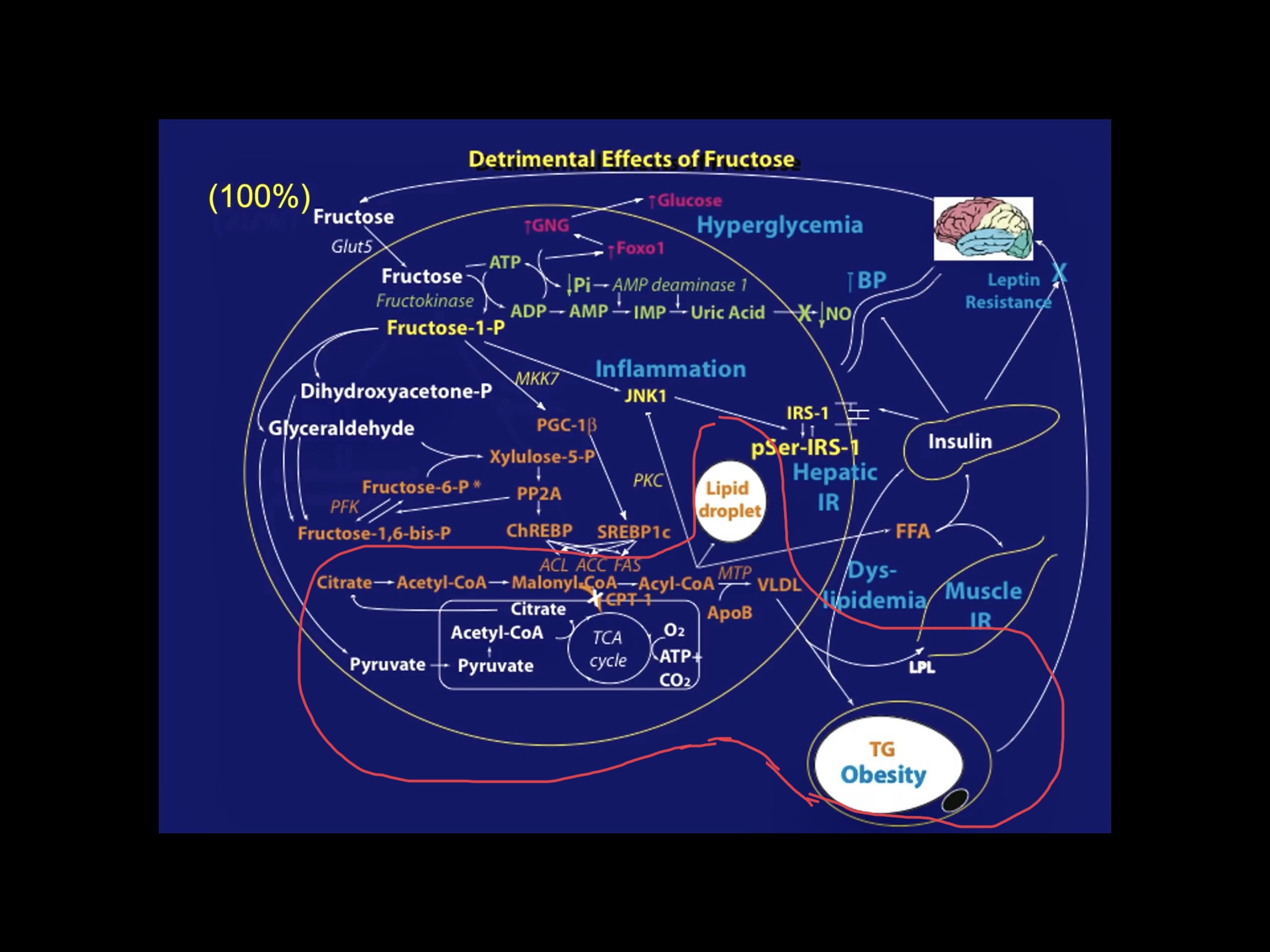
Fructose is a component of sucrose which has no effect on blood glucose levels but must be delivered to the liver for digestion. Excessive liver digestion is another factor that can slow the fat loss process and lead to other problems as well.
Moderation is always key but consumption of the wrong type of fruits while dieting may not be optimal for losing fat long term.
/88168950-56a6b4603df78cf7728fd2f5.jpg)
Fruits to Be Avoided While Losing Fat
Fruits are almost similar to supplements because they’re beneficial for replacing missing essentials in the diet.
The fiber content from most fruits increase satiety and lower appetite after meals, which is crucial for losing body fat. This specifically applies to fruits lower on the glycemic index.
The glycemic index indicates how quickly a fixed amount of food is converted to glucose in the body. The lower range on the scale is less than 55, mid range 56-69, and the high range is over 70.
Glycemic load on the other hand refers to how much a non-fixed amount of food increases blood glucose, multiplying the glycemic index by the total carbohydrates. Fiber greatly reduces the glycemic load, which makes fruits great for weight management.
However, not all fruits are structured the same as some have higher amounts of fiber than others.
When observing the wide varieties for consumption, melons have the highest sugar content with the lowest fiber per gram. Dried fruits are also high in sugar because the water content has been reduced and the carbohydrate molecules are more concentrated.
It’s also easier to become addicted to high glycemic foods as they target a region in the brain known as the nucleus accumbens. When displayed on a MRI scan this area lights up when foods high in sugar are consumed.
Because some fruits have higher sugar content than others , it’s important to observe the effect of fructose on the body. While glucose can be digested and utilized by nearly all the cells in the body, fructose can only be digested by the liver organ.
Once fructose enters the the body, the hepatic cells go through the Krebs cycle, which creates byproducts of triglycerides that can build up in the liver or visceral tissues of the body.
While eating more common or tropical fruits won’t likely increase the work load of the liver, consumption of fruits would have to be in excess to amounts of sugar found in soda, candy, and desserts (see Does Eating Too Much Fruit Make You Fat?).
How to Add Fruits to Your Fat Loss Diet
The most important factor in regards to meals is not the glycemic index, but the glycemic load. Glycemic load takes into account all of the foods that are consumed as a whole, especially when fiber is included in the meal.
Glycemic load ranges start at low, which is less than 10, 11-20 for moderate, and greater than 20 for high.
A fruit can have a high glycemic index but a relatively low glycemic load, such as watermelon for example. These are the fruits that are ok to consume on a fat loss diet.
The fruits to avoid when targeting fat loss are those highest on the glycemic load index: figs, dates, raisins. This also includes all other dried fruit as the sugar content will be much more concentrated than its natural form.
If a high glycemic index/low fiber fruit is consumed it should be paired with a protein or an unsaturated fat to slow the amount of carbohydrate released into the bloodstream.
For example, avocado, coconut oil, or olive oil are great additions to a meal eaten with a fruit higher on the glycemic index scale. Overall glycemic load is what matters the most on a diet.
The Wrap Up
Fruits are natural source of nutrients with varying amounts of sugar, which why they should be consumed with precaution while dieting. It’s unlikely fruit will be create metabolic syndrome or insulin resistance in any one individual, but fruit is not optimal choice for removing fat from the body either. Manage the glycemic load of your meals in a fat loss diet by avoiding dried fruits and pairing meals with protein and healthy unsaturated fats.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.