No Clue How to Lose Weight
The biggest problem many people have concerning their health is the management of their weight.
It’s not hard to figure out why, access to calorically dense foods are easier than ever and an over saturation of weight loss information posted online makes it too confusing to resolve on your own.
With a large percentage of the general population trying to lose weight as fast as possible, there’s a slew of diets you can try, each one claiming to be better than the last.
The problem is that of the people who are currently on some kind of diet (something like 45 million people at any given time) only 5% of them will keep the weight off.
A lot of factors come into play with losing weight, but one of the biggest reasons why the weight may come back for some is due to how fast the weight was lost.
Losing weight at a faster pace than what is recommend comes with a price, usually having worse results that you expected and frustration that can cause you to doubt your ability to keep the weight off.

How Much Weight Should You Lose In A Week
There’s nothing worse than going through a long, tedious process just to cycle back to where you started every time. This is what typically happens when you choose to start crash dieting.
Crash dieting involves a severe caloric deficit with a much smaller consumption of meals in ratio to calories expended from from exercise and/or the resting metabolic rate.
Dieting in this manner drops the weight faster than smaller calorie deficits of 500 calories or less per day.
The problem with severe calorie restriction diets is that it causes the body’s metabolism to dramatically slow down.
Dropping caloric intake far below levels needed to maintain your body weight changes the homeostasis of the body, which impacts hormones released that affect your hunger, feelings of fullness after meals, and ability to maintain your weight.
Restricting calories far below a certain threshold level also affects the amount of lean muscle mass. Large caloric deficits over a period of time creates a stressful environment in the body, which releases one of the body’s ‘flight or fight’ response hormones, cortisol.
Cortisol helps release energy for your body by breaking down protein and converting it into glucose in a process known as gluconeogenesis.
This is the reason why studies show that athletes retained more muscle when they consumed higher amounts of protein than the regular recommended amounts.
This gradual muscle breakdown gives a poor impression in weight loss progress photos, as the dieter often fails to recomposition the body with lean muscle and lower body fat levels. Typically this results in a smaller frame with more work needed to ‘tone’ or contour their frame.
An example of this:
What’s more important is the type of weight you lose and where that weight was lost.
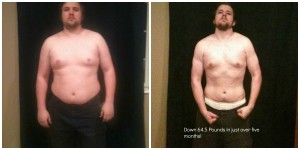
Here’s an example of weight lost the right way:

Weight came off the right way. Before he started he was overweight but shows how a proper diet and exercise regiment is supposed to look like. Visible definition in the midsection and the arms.
The faster you lose weight the more you pay for it in the long term.
The “skinny fat” look comes from a combination of two things: concentrating on too much aerobic exercise while dropping weight and restricting calories too much.
Whenever you restrict more than 500 calories under your TDEE (total daily energy expenditure), you’re more likely to strip away muscle along with the fat that you didn’t want.
For example, someone with a TDEE of 3000 calories restricting their calories down to 2000 calories would lose more lean muscle mass than someone losing weight at 2500 calories.
Eventually the person losing weight would stop losing weight at 2500 calories, so they would have to decrease their calories to 2400. The difference is that calories restricted is VERY gradual, giving time to make small changes to the diet as weight loss slows down.
If you want to lose weight the right way, focus on losing 1-2 pounds a week AT THE MOST. If an individual is overweight or obese (body mass index over 30) losing 2-3lbs per week is also reasonable to keep good a body composition as the weight is coming off.
The Wrap Up
Rapid weight loss has become popular and trendy, but it comes with a price in the long term. Strict dieting for even a short period of time greatly changes your body’s hormonal response, which makes the diet harder to commit to and possible to gain the weight back. Even if you’re “clinically overweight” for your height, you should lose weight gradually until you reach your target weight. Diet and exercise are necessary for weight loss, but you have to do it the right way for lasting results.